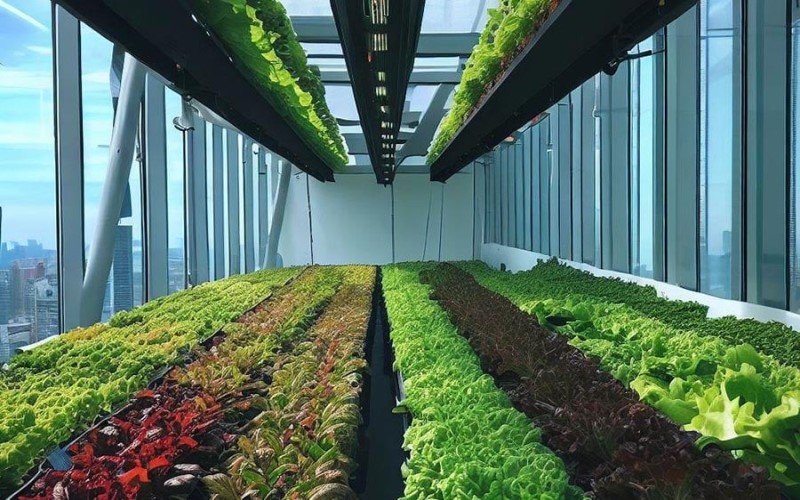
Imagine a world where fresh produce is harvested just steps away from your doorstep, eliminating the need for long supply chains and reducing carbon footprints. This isn’t some futuristic dream; it’s the reality of vertical farming. As urban areas expand and the demand for food rises, innovative methods like these are stepping into the spotlight.
Vertical farming redefines how we think about agriculture in cities. It’s not just about growing crops indoors; it’s about revolutionizing our approach to sustainability and food security real money blackjack. With skyscrapers filled with greens instead of concrete, could this be the answer to our urban food dilemmas? Let’s explore what vertical farming truly entails and whether it can sustain our ever-growing populations while preserving our planet’s health.
What is Vertical Farming?
Vertical farming is an innovative approach to agriculture that maximizes space by stacking layers of crops. Instead of sprawling fields, this method utilizes vertical structures—think warehouses or skyscrapers—to cultivate food.
Employing advanced techniques like hydroponics and aeroponics, vertical farms grow plants without soil. Nutrient-rich water solutions provide everything the crops need for healthy growth.
This method not only saves land but also allows year-round production regardless of external weather conditions. With controlled environments, factors like light, temperature, and humidity are optimized to boost yields.
Moreover, vertical farming can be integrated into urban areas where traditional farming isn’t feasible. It brings fresh produce closer to consumers while minimizing transportation emissions. As cities grapple with limited arable land and increasing populations, this innovative solution could redefine our relationship with food production in urban settings.
Advantages of Vertical Farming
Vertical farming offers a range of compelling benefits. It maximizes space efficiency. By stacking layers of crops, urban areas can harness unused vertical spaces like warehouses and rooftops.
Another advantage is resource conservation. Vertical farms typically use hydroponics or aeroponics, requiring significantly less water than traditional agriculture. This is crucial in regions facing water scarcity.
Additionally, they facilitate year-round crop production. Controlled environments protect plants from harsh weather conditions and pests, leading to consistent yields regardless of the season.
Moreover, reduced transportation distances mean fresher produce for consumers. This not only enhances flavor but also lowers carbon emissions linked to food transport.
Vertical farming has potential for job creation in urban settings. As these facilities grow in popularity, they bring new employment opportunities through tech development and agricultural management roles.
Challenges and Limitations
Vertical farming, while innovative, faces several challenges that can hinder its growth. Initial setup costs are high. Building a facility requires significant investment in technology and infrastructure.
Energy consumption is another concern. Many vertical farms rely on artificial lighting and climate control systems, which can lead to substantial electricity bills. This raises questions about the sustainability of operations if energy sources are not renewable.
Limited crop diversity presents further limitations. Not all plants thrive in controlled environments. Some crops simply require more space or different conditions than vertical farms can provide.
Moreover, market acceptance remains an issue furmintusa.com. Consumers often perceive traditionally grown produce as fresher or tastier compared to those grown indoors.
Scalability poses a challenge for many urban areas trying to implement these systems effectively without compromising quality or efficiency.
Environmental Impact
Vertical farming significantly reduces the environmental footprint of traditional agriculture. By utilizing controlled indoor environments, it minimizes water usage drastically—up to 90% less than conventional methods. This is a game changer in regions where water scarcity poses major challenges.
Energy consumption remains a concern, but innovations like LED lighting and renewable energy sources are making strides. Farms can now harness solar power or wind energy, further lowering their carbon emissions.
Pesticide use also sees a notable decline in vertical systems. With climate-controlled settings, there’s less need for harmful chemicals that often leach into soil and waterways.
Additionally, local production cuts transportation costs and associated emissions. When food doesn’t have to travel across states or countries, its freshness improves while pollution decreases—a win-win for urban ecosystems.
This sustainable approach not only feeds people but also contributes positively to urban biodiversity when integrated thoughtfully into city landscapes.
Urban Food Supply Crisis
The urban food supply crisis is a pressing issue that affects cities worldwide. Rapid population growth and increasing urbanization have outpaced the capacity of traditional agriculture. Many metropolitan areas find themselves reliant on distant farms, leading to longer shipping times and higher carbon footprints.
Food deserts are becoming more prevalent, where communities lack access to fresh produce. This has serious implications for public health, as processed foods fill the void. Malnutrition and related diseases become rampant in these environments.
Additionally, climate change poses significant threats to agricultural productivity. Extreme weather events disrupt harvests while changing growing seasons make it harder for farmers to keep up with demand.
As cities expand and resources dwindle, innovative solutions are essential. A sustainable approach must bridge the gap between food production and consumption within urban landscapes.
Success Stories of Vertical Farms
Vertical farming is not just a concept; it’s becoming a reality in various urban centers around the globe. One notable success story comes from Brooklyn Grange, which operates rooftop farms in New York City. They grow organic produce while utilizing sustainable practices, demonstrating how urban spaces can be transformed into green havens.
Another impressive example is AeroFarms, based in Newark, New Jersey. This company harnesses aeroponic technology to cultivate leafy greens without soil and with minimal water usage. Their innovative approach has garnered attention and investment, proving that vertical farms can thrive even in densely populated areas.
Then there’s Plenty, located in San Francisco’s Bay Area. By using advanced data science and artificial intelligence, they create optimal growing conditions for crops indoors. Their model showcases efficiency while addressing food accessibility issues within cities.
These ventures illustrate the potential of vertical farming as an answer to modern agricultural challenges amid urbanization.
The Future of Vertical Farming and its Potential
The future of vertical farming holds significant promise for addressing urban food supply challenges. As cities continue to grow, the demand for fresh produce increases. Vertical farms can meet this need by utilizing innovative technologies and efficient use of space.
Advancements in hydroponics, aeroponics, and smart agriculture are transforming how we think about food production. These systems allow crops to thrive without traditional soil while using considerably less water than conventional farming methods.
Moreover, as sustainability becomes a priority globally, vertical farms contribute positively to reducing carbon footprints associated with transporting food across long distances. They also enhance local economies by creating jobs within urban centers.
Collaboration between governments and private entities could further accelerate the growth of this industry. Supportive policies might encourage investment in research and development that drives innovation forward.
As public awareness about sustainable practices grows, consumers increasingly seek out locally sourced products. This trend aligns well with what vertical farming offers — fresh greens delivered right from farm to table within city limits.
Vertical farms not only provide an alternative method of cultivation but also present opportunities for educational programs regarding agriculture’s role in society today. Engaging communities through workshops or tours can foster understanding around where their food comes from.
With continued technological advancements and a growing commitment toward sustainability, vertical farming has the potential to become an integral part of our urban landscapes—reshaping how we produce and consume food moving into the future.