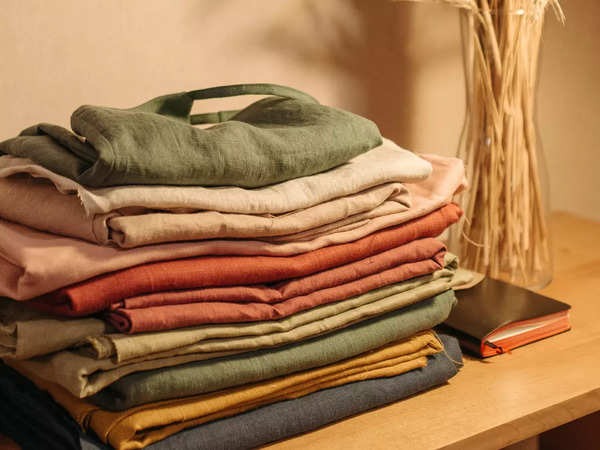
Cotton has been a cornerstone of the textile industry for centuries, and its journey from farm to fashion is a remarkable story of human ingenuity and collaboration. Cotton fabrics have been an integral part of the global textile trade, and in recent years, Indian cotton fabric wholesalers have played a significant role in this industry. In this article, we will explore the fascinating journey of cotton fabrics, from their cultivation in fields to their distribution by wholesalers, with a focus on the role of Indian cotton fabrics wholesaler.
The Origin of Cotton:
Cotton’s history can be traced back to ancient civilizations, with evidence of cotton cultivation and use dating back to 2500 BC in the Indus Valley, which is part of present-day India and Pakistan. Cotton was highly prized for its softness, breathability, and versatility, making it an ideal choice for textiles. Over time, cotton cultivation spread to various parts of the world, including Egypt, China, and the Americas, through trade and exploration.
Cotton Cultivation:
The journey of cotton fabrics begins in the cotton fields, where this natural fiber is cultivated. Cotton is a tropical and subtropical crop that requires specific growing conditions, including warm temperatures, ample sunlight, and well-drained soil. In India, cotton cultivation has a long history and remains a vital agricultural sector. The country is known for producing high-quality cotton, which is used in the manufacturing of a wide range of textiles.
Indian cotton fabric wholesalers rely on a network of cotton farmers across the country to supply them with raw cotton. These farmers work tirelessly to nurture the cotton plants, carefully tending to them throughout the growing season. Modern cotton farming often incorporates sustainable and eco-friendly practices to minimize the environmental impact, including reduced pesticide use and water conservation efforts.
Cotton Processing:
Once harvested, the cotton goes through a complex processing journey to transform it from fluffy cotton bolls into the smooth, thread-like fibers needed for textiles. This process involves several stages, including ginning, carding, and spinning.
Ginning is the initial step where cotton fibers are separated from the seeds and other debris. This process results in a clean and fluffy mass of cotton fibers known as “lint.” Carding follows, where the cotton fibers are aligned and combed to create a uniform strand of fibers. Finally, spinning transforms these fibers into yarns, ready to be woven into fabrics.
Weaving and Manufacturing:
The next phase in the journey of cotton fabrics involves weaving and manufacturing. Weaving is the process of interlacing the cotton yarns to create a fabric structure. This step can vary in complexity, from traditional handloom weaving to modern, high-speed mechanical looms. The choice of weaving method often depends on the desired fabric type and its intended use.
Indian cotton fabrics are known for their exquisite craftsmanship and intricate designs. Skilled artisans and textile workers are responsible for creating a wide range of cotton fabrics, from traditional handwoven sarees to contemporary garments and home textiles. The diversity of Indian cotton fabrics showcases the rich cultural heritage and artistic traditions of the country.
Role of Cotton Fabrics Wholesalers:
Cotton fabrics wholesalers play a pivotal role in the textile supply chain. They act as intermediaries between cotton manufacturers and retailers, ensuring a seamless flow of cotton fabrics into the market. Wholesalers source cotton fabrics from various manufacturers, including textile mills and small-scale artisans, to build a diverse and comprehensive product catalog.
Indian cotton fabrics wholesalers have gained prominence in the global textile industry due to the high quality and unique designs of Indian cotton textiles. They cater to both domestic and international markets, supplying cotton fabrics to garment manufacturers, retailers, and individual customers. These wholesalers often collaborate with designers and fashion brands to create exclusive collections that showcase the beauty of Indian cotton fabrics.
Global Distribution and Sustainability:
Cotton fabrics, including Indian cotton fabrics, are distributed worldwide to meet the demands of fashion-conscious consumers. The global supply chain for cotton fabrics involves transportation, warehousing, and logistics to ensure timely delivery to retailers and consumers.
In recent years, there has been a growing emphasis on sustainability in the textile industry. Cotton fabrics wholesalers are increasingly adopting eco-friendly practices, such as sourcing organic cotton, reducing waste in production, and implementing ethical labor practices. Sustainability initiatives not only benefit the environment but also appeal to consumers who are becoming more conscious of their purchasing choices.
Challenges and Innovations:
The journey of cotton fabrics is not without its challenges. Factors such as weather conditions, pest infestations, and fluctuations in cotton prices can impact cotton cultivation. Additionally, the textile industry faces competition from synthetic fibers and changing consumer preferences.
To address these challenges, cotton fabric wholesalers are embracing innovation. They are exploring new dyeing and finishing techniques to create unique and sustainable fabrics. Advances in technology have also led to the development of smart textiles with properties like moisture-wicking, UV protection, and antimicrobial features.
Conclusion:
The journey of cotton fabrics, from farm to fashion, is a testament to human creativity and adaptability. Indian cotton fabrics wholesalers play a vital role in bringing the beauty of Indian textiles to the world, contributing to the growth of the global textile industry. As sustainability becomes increasingly important, the textile industry is evolving to meet the demands of environmentally conscious consumers while preserving the timeless appeal of cotton fabrics. The future of cotton fabrics wholesaling promises to be both innovative and sustainable, ensuring that this natural fiber continues to be a cornerstone of the fashion industry for generations to come.