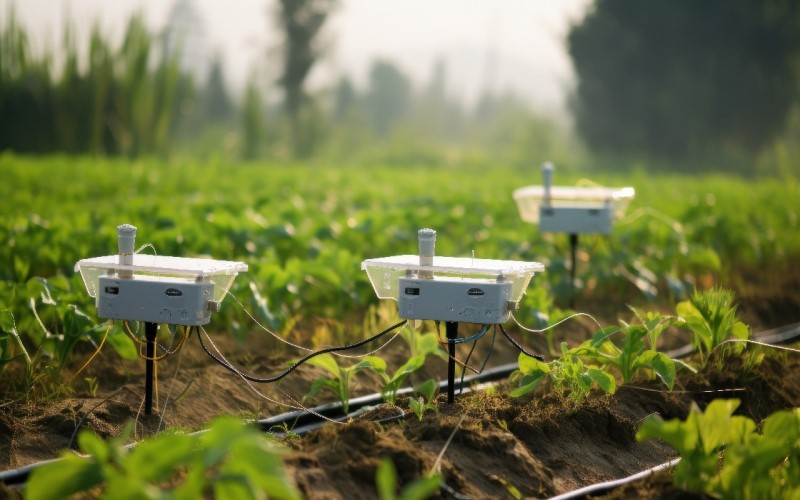
Introduction to Irrigation Technology and its Importance
Water is one of our planet’s most precious resources, yet it often goes to waste in the quest for lush gardens and thriving crops. As climate change intensifies and water scarcity becomes a pressing concern, innovative irrigation technologies have stepped onto the stage view more. These advancements are not just about improving crop yields; they play a crucial role in preserving our environment. Embracing modern solutions can lead to more sustainable agriculture while ensuring that every drop counts.
Gone are the days when farmers relied solely on traditional methods that often wasted more water than necessary. Today’s innovations offer smarter ways to nurture plants while minimizing resource consumption. Join us as we explore how cutting-edge irrigation technology can transform farming practices and contribute to effective water conservation strategies. The future of agriculture is here—and it’s time to dive into these exciting developments!
Traditional Irrigation Methods vs Modern Innovations
Traditional irrigation methods have served farmers for centuries. Techniques like surface and flood irrigation are still in use today. They rely heavily on gravity to distribute water across fields. While effective, they can be wasteful, leading to evaporation and runoff.
In contrast, modern innovations focus on efficiency and precision. Technologies such as drip irrigation deliver water directly to plant roots. This method minimizes waste by targeting the areas that need it most.
Another advancement is the integration of technology with traditional practices. Smart systems monitor weather data and soil conditions in real time. By doing so, they optimize water usage based on actual needs rather than assumptions.
The shift from age-old techniques to contemporary solutions showcases a growing awareness of sustainability within agriculture. Farmers are adapting not only for crop health but also for environmental stewardship.
Drip Irrigation System: A Water-Efficient Solution
Drip irrigation is a game changer for farmers and gardeners alike. This innovative system delivers water directly to the roots of plants, minimizing waste. By using a network of tubing, emitters release small amounts of water precisely where it’s needed.
This targeted approach not only conserves water but also enhances plant health. The soil remains moist without becoming overly saturated, reducing the risk of root rot.
Another advantage is its adaptability. Drip systems can be customized for various terrains and crops, making them suitable for diverse agricultural environments.
Moreover, they promote deeper root growth as plants seek moisture below the surface. This results in stronger and more resilient vegetation that can better withstand drought conditions.
Investing in drip irrigation technology benefits both the environment and crop yield. It’s an efficient way to ensure sustainable farming practices while maximizing productivity.
Smart Irrigation Controllers: Making Water Conservation Easier
Smart irrigation controllers are revolutionizing how we manage water in agriculture and landscaping. These devices utilize weather data, soil conditions, and plant needs to optimize watering schedules.
Gone are the days of guesswork. With smart controllers, you can automate your irrigation system based on real-time information www.onyxplatform.org. If rain is on the way, they adjust accordingly, preventing unnecessary water waste.
Many models connect to smartphones or tablets through apps. This means users can monitor their systems from anywhere, making adjustments with a tap of a finger.
Not only do these systems conserve water, but they also promote healthier plants by delivering moisture exactly when needed. Gardeners and farmers alike are finding that this technology leads to both environmental benefits and cost savings over time.
Investing in smart irrigation is not just about saving water; it’s about being part of a sustainable future for our planet’s resources.
Soil Moisture Sensors: Saving Water and Plants
Soil moisture sensors are revolutionizing the way we approach irrigation. These devices measure the water content in the soil, allowing farmers to understand exactly when their crops need watering.
By providing real-time data, these sensors help prevent overwatering. This not only conserves precious water but also promotes healthier plant growth. Overly wet soil can lead to root rot and other issues; moisture sensors help avoid such problems.
The technology is becoming increasingly user-friendly. Many models now connect to smartphones, offering notifications and updates at your fingertips.
Farmers can make informed decisions based on accurate readings instead of relying solely on guesswork or outdated techniques. With this precision farming approach, they can optimize their resources effectively.
These advancements contribute significantly to sustainable agriculture practices while ensuring that plants receive just the right amount of hydration.
Crop Selection and Rotation for Efficient Irrigation
The choice of crops plays a significant role in irrigation efficiency. Selecting drought-resistant varieties can significantly reduce water usage. These plants are specially bred to thrive with less moisture, making them ideal for regions prone to dry spells.
Additionally, crop rotation is an effective strategy that enhances soil health and optimizes the use of available water. By alternating crops, farmers can prevent nutrient depletion and improve soil structure. This practice not only conserves water but also supports sustainable agriculture by reducing pest populations and disease cycles.
By being strategic about what to plant and when, growers can ensure their fields remain productive while using far less water than traditional methods would require. Adapting these practices offers a win-win situation: healthier ecosystems and enhanced yields with minimal resource waste.
Embracing innovative approaches in crop selection and rotation sets the stage for smarter irrigation strategies that align agricultural needs with ecological sustainability.