Buying a house is a significant milestone in many people’s lives, but it often requires securing a mortgage, which, in turn, involves assessing your creditworthiness. Your credit score is a crucial factor that lenders consider when determining your eligibility for a mortgage and the terms they can offer you. So, what credit score do you need to buy a house? Let’s explore the key factors that influence your ability to secure a home loan.
The Role of Credit Scores: Credit scores are numerical representations of an individual’s creditworthiness. They reflect a person’s credit history, including their borrowing and repayment habits. These scores help lenders assess the risk associated with lending money to a borrower.
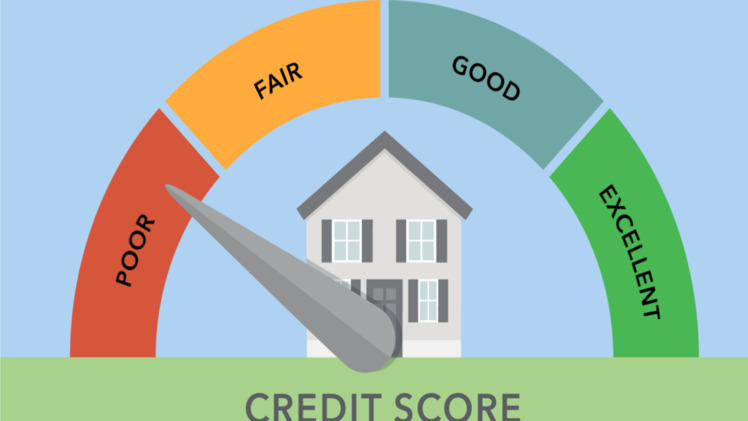
Credit Score Ranges: Credit scores typically range from 300 to 850. Here’s a general breakdown of the credit score categories:
- Poor (300-579)
- Fair (580-669)
- Good (670-739)
- Very Good (740-799)
- Excellent (800-850)
Minimum Credit Score for a Mortgage
The minimum credit score required to buy a house varies depending on the type of mortgage and the lender. Here’s a general guideline:
FHA Loans: The Federal Housing Administration (FHA) offers loans to individuals with lower credit scores. You can often qualify for an FHA loan with a credit score of around 580. Some lenders may even consider borrowers with scores as low as 500 but may require a higher down payment.
Conventional Loans: Conventional loans, not backed by the government, typically require higher credit scores. A credit score of 620 or higher is often the minimum for a conventional mortgage, although lenders may have specific requirements.
VA Loans: If you’re eligible for a loan from the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA), credit score requirements are generally more flexible. Many VA lenders look for a credit score of at least 620, but some may accept lower scores.
USDA Loans: The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) offers loans for rural homebuyers. Credit score requirements vary but generally start at around 640.
Jumbo Loans: Jumbo loans, which exceed the conforming loan limits set by Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac, often require higher credit scores. Lenders may expect scores of 700 or more for jumbo mortgages.
Credit Score Impact on Mortgage Terms
Your credit score doesn’t just determine whether you can qualify for a mortgage; it also affects the terms you’ll receive. A higher credit score typically results in better loan terms, such as lower interest rates, lower down payments, and reduced fees. Conversely, lower credit scores may result in less favorable terms, including higher interest rates and larger down payments.
Improving Your Credit Score: If your credit score falls below the desired range for a mortgage, there are steps you can take to improve it:
Pay Bills on Time: Consistently making on-time payments is one of the most effective ways to boost your credit score.
Reduce Debt: Paying down outstanding debts, especially credit card balances, can positively impact your credit score.
Check Your Credit Report: Regularly review your credit report for errors or inaccuracies and dispute any discrepancies you find.
Avoid Opening New Credit Accounts: Opening too many new credit accounts within a short period can negatively affect your credit score.
Diversify Your Credit Mix: A mix of different types of credit, such as credit cards, installment loans, and retail accounts, can benefit your credit score.
In conclusion, the minimum credit score required to buy a house depends on the type of mortgage and the lender. FHA loans offer more leniency for lower credit scores, while conventional loans typically have higher standards. A better credit score not only improves your chances of mortgage approval but also leads to more favorable terms. If your credit score isn’t where you want it to be, taking steps to improve your credit can help you secure a better mortgage offer and make your dream of homeownership a reality.